Description
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) offers numerous benefits including storage of water.
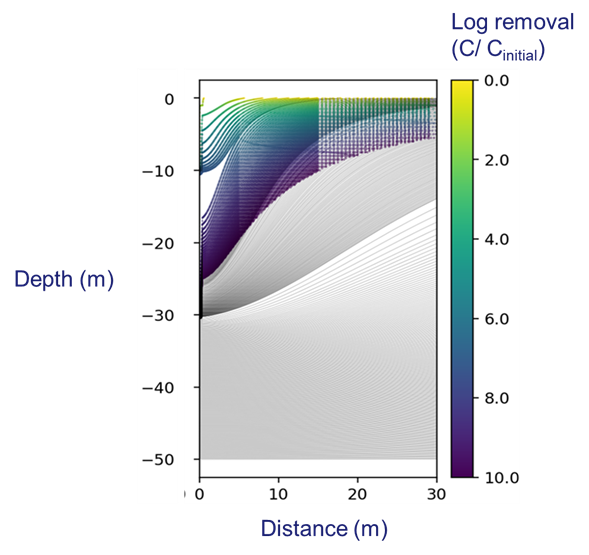
- The source water for MAR schemes is often contaminated with pathogens.
- One of the advantages of MAR, is that the pathogens may be removed during storage and transport
Challenge
- Existing models for pathogen removal require high expertise (e.g., Hydrus 2D) or are not suited for MAR-applications (QMRAwell)
- Removal parameters are hard to estimate
- Depend on organism related properties (e.g., diameter, survival rate)
- Environmental parameters such as temperature, redox conditions, and flow rate
- Existing databases are not tailored to conditions typical for MAR conditions
The aim of this tool is to retrieve plant pathogen transport properties and use this information to predict concentration of pathogens after subsurface storage.
Target audience
Direct users:
Professionals involved in the design (e.g., engineers) or in evaluation of MAR-schemes (e.g., health experts, pest control experts)
Owner of the product
Sign in to access this information.Actors, their roles and interactions
Indirect beneficiaries:
- Agricultural companies -> less risk of plant diseases,
- MAR-Technology providers-> more optimal dimensioning of MAR-schemes
Unique selling points
Simple method to get a first estimate of microbial risks of Managed Aquifer Recharge.
Technical requirements
Computer with Python version 3.6 or higher installed.
Software data
| First version | |
| 2022 | |
| MIT License |
URL
https://sutra.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial.html
Technologies applied by the product
Controlled artificial recharge and drainage (CARD) system
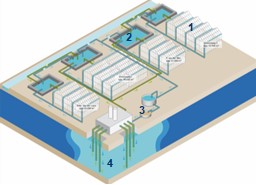
Large scale Aquifer Storage & Recovery (ASR) Systems
Large scale Aquifer Storage & Recovery (ASR) systems are human-made or human-enhanced natural systems that harvest (e.g…

